You are likely to be familiar with the 404 error code which tells you the webpage you are looking for hasn’t been found. But did you know using this error message in the wrong context can generate what’s known as a soft 404, which can impact your SEO performance?
Marketers sometimes overlook such technical aspects of websites and expect web developers to handle them instead. This can be detrimental to a website’s performance in search results, which is why SEO specialists need to work closely with web developers.
This article will focus on one particular category of crawl error, one that, if left unresolved, can hugely reduce the amount of pages search engines such as Google crawl and index in their search results. In this article, we will cover:
- What a soft 404 error is
- The problems with soft 404 errors
- How to fix soft 404 errors
- Why fixing soft 404 errors will help your website’s performance
What’s a Soft 404 Error?
A true 404 error message occurs when a website’s server returns an HTTP 404 standard response code to indicate that it couldn’t find the webpage (URL) that was requested by the user. This informs both browsers and search engines that the page doesn’t exist.
What most people don’t understand is that the content of the page – ‘page not found’ message – is entirely unrelated to the HTTP response returned by the server. Just because a page displays a 404 File Not Found message, it does not mean that this page is automatically defined as a 404 page.
In Google’s own words: “This is like a giraffe wearing a name tag that says ‘dog’. Just because the name tag says it’s a dog, doesn’t mean it’s actually a dog. Similarly, just because a page says 404, doesn’t mean it’s returning a 404 status code.”
A soft 404 error occurs when a non-existent page (a page that has been deleted/removed) displays a ‘page not found’ message to anyone trying to access it but fails to return an HTTP 404 status code. They can also occur when the non-existent page redirects users to an irrelevant page, such as the homepage, instead of returning an HTTP 404 status code.
The important thing to remember here is that the content of a web page is entirely unrelated to the HTTP response returned by the server.
This distinction is important for SEO because it determines how Google treats the page. Crawling and indexing is a process Google’s bots go through before listing your website’s pages in search engine result pages. When a true 404 error message is returned, Google’s bots don’t spend time crawling or indexing the page. When a soft 404 error is returned the page is still crawled and indexed.
The Problem With Soft 404 Errors
If your website returns an HTTP status code other than a 404 (or 410) for a non-existent page, it can negatively impact the website’s performance in organic search. This means that if your website has a high proportion of soft 404 errors, it can be harmful. By failing to serve a 404 status code, your website is telling search engines that there’s a real page at the URL they’re attempting to access. As a result, the URL you’ve deleted (with no content) will be crawled and indexed, thus wasting valuable crawl budget on redundant pages.
Google defines Crawl Budget as “the number of URLs Googlebot can and wants to crawl.” Crawl Budget is split into Crawl Rate and Crawl Demand:
- Crawl Rate – Designed to help Google not crawl your pages too frequently or too fast and hurt your server
- Crawl Demand – How much Google wants to crawl your pages. This is based on how popular your pages are and how stale the content in Google’s index is
Google doesn’t want to waste endless time crawling content on the same website, so it makes sense for them to assign a ‘budget’ to their web crawls before moving on to another website.
Sticking with the idea of crawl budgets, if a website has a high proportion of soft 404 errors, then those pages will be crawled. The process of crawling these non-existent pages will invariably take up needless amounts of the crawl budget assigned to the site. Because of the time Googlebot spends crawling soft 404s, your unique URLs may therefore not be discovered as quickly or crawled as frequently – thus reducing the visibility of the important content on your site.
Ultimately, if you have a high percentage of soft 404s, you’re not only wasting crawl budget on meaningless pages, but you’re also reducing the visibility of your important pages. It should, therefore, come as no surprise that when soft 404 errors are resolved, the performance of a website in organic search results tends to improve.
To explain how you’d assess the extent of a soft 404 issue, let’s take a look at an example of a website that is displaying a number of soft 404 errors in Google Search Console. In the example below, we see 147 soft 404 errors being reported for the website in question. This may well cause alarm bells to ring, but we first need to consider the figure in context.
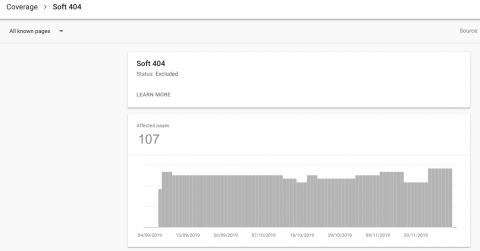
To do this, we need to check how many webpages on the website have been submitted to Google to crawl and index. For this task, we’d take a look at the XML sitemap for the website in question – which is a key indicator of how many pages a website has. You can see which XML sitemaps have been submitted under Search Console > Sitemaps
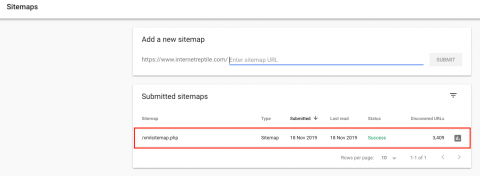
And the coverage, which shows how many webpages are being indexed or have any issues can be found under Search Console > Coverage > Find XML sitemap in the dropdown
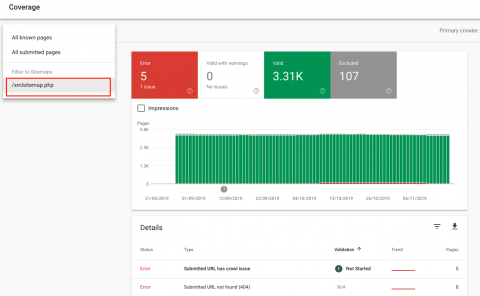
The example above shows that Google is indexing 3.31K pages of content from the website in question.
Looking at the data above, we can see that this website has around 3,409 pages, so the 107 soft 404 errors now start to seem a little less ominous. Still, at over 3% of the site’s total pages, the 107 soft 404 errors are still wasting some of the crawl budget assigned to this website. In this case, Google is spending too much time crawling URLs that simply don’t exist.
How Do I Resolve These Issues?
Google only lets you export a maximum of 1000 URLs in Google Search Console. In the example above, there are under 1000 errors being reported, so these can be downloaded directly via Search Console. Once you’ve exported the list of URLs, you’ll need to assess why the pages are being reported as soft 404s. Google provides some information on the URLs they highlight as soft 404s, as you can see in the example below:
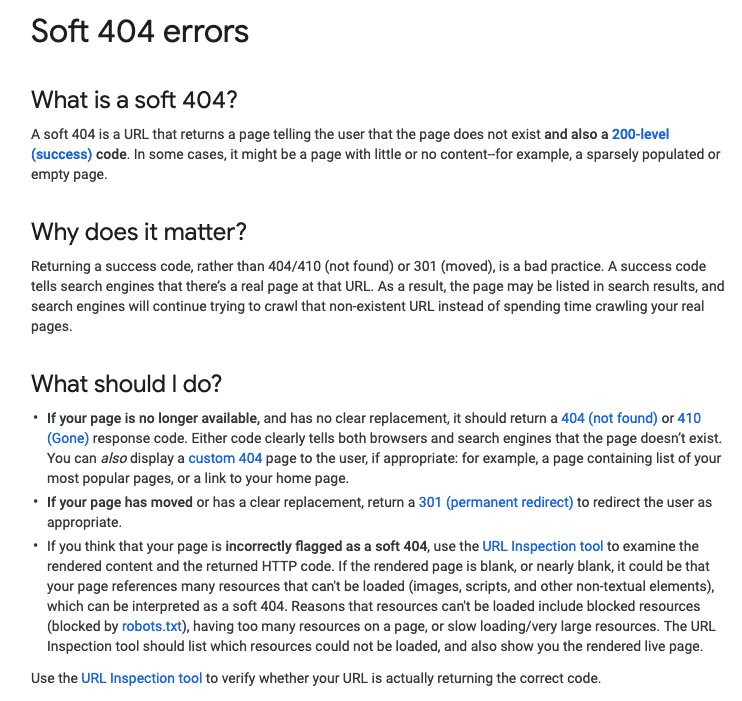
In most cases, you will find that a website will be serving a 200 (OK) status code on pages that return a “page not found” message. Therefore, the first thing you’d need to do is run a selection of the soft 404 error pages through an HTTP status code checker such as httpstatus.io, to assess which status codes those pages are returning.
Let’s say the example domain below was displaying a 404 page to the user trying to access it, but when we checked the response code using an HTTP status code checker, it returned an HTTP 200 response. This is a prime example of a soft 404 error, as the HTTP response code is indicating to search engine robots that the page exists and should be crawled. However, there is no content on the page that’s returned by the server.
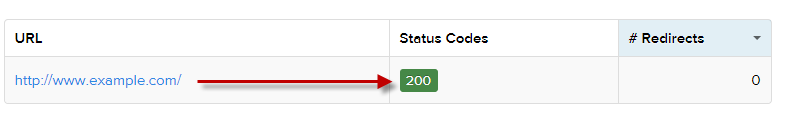
Page returning an HTTP 200 server response code. Checked using: https://httpstatus.io/
The other issue you might encounter when diagnosing the root cause of soft 404 errors, is inappropriate 301/302 redirects.
301 redirects should be used when a page is permanently deleted and you want to send people to a new more appropriate page. 302 redirects are similar to 301s but are used when the page is temporarily deleted.
Some webmasters choose to redirect all deleted pages to the website’s homepage instead of serving a 404 error, which is not at all appropriate and confuses search engine robots. It’s important to highlight having 404s on your website isn’t a bad thing. Deleted pages or out of stock products should only be redirected to a direct replacement. If a direct replacement doesn’t exist then you should serve a custom 404 error page to display alternative options or products to the user.
I have highlighted an example of inappropriate redirects triggering soft 404 errors below. In this case, the webmaster is using 302 redirects to redirect anyone trying to access a page that’s been deleted, and redirecting those users to a custom 404 page – one which doesn’t actually serve an HTTP 404 status code. This will hugely impact how search engines crawl the website in question, as search engines are being instructed to look elsewhere for pages that have actually been deleted. If a search engine robot follows those instructions, they will eventually be served an HTTP 200 (OK) status code for a page that displays a 404 error message, which is a whole other level of bad practice.
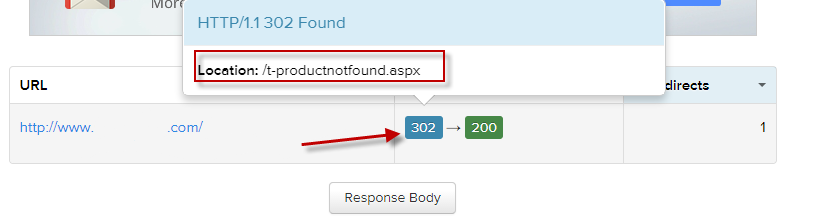
An example of a 302 redirect being used to send users to a custom 404 error page
You should never use redirects to serve a 404 error page. Instead, serve an HTTP 404 response code when any pages you remove or delete from your website are requested and there is no direct replacement. This will prevent your website triggering a huge number of soft 404 errors and will ensure search engines only crawl and index the pages you want to rank.
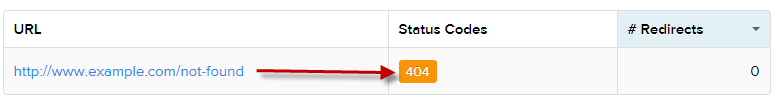
Page returning an HTTP 404 server response code. Checked using: http://httpstatus.io/
Will Solving Soft 404 Errors Increase Traffic to My Website?
The results of a technical SEO project we once worked on for an e-commerce client made it very clear why you should always take note of soft 404 errors. We noticed the client in question had an extremely high proportion of soft 404 errors compared to the total number of pages on their site. We discovered this was because their website was serving 404 messages without returning HTTP 404 status codes for many of their deleted products, of which there were thousands.
Once we’d diagnosed the issue, we liaised with the client’s web developer to ensure their server returned HTTP 404 status codes alongside the ‘page not found’ messages for any products they’d removed from their website. The developer implemented the fix as we suggested, and two days later, we noticed organic traffic had increased dramatically. It rose from an average of 1,400 sessions per day to an average of 2,600 per day.
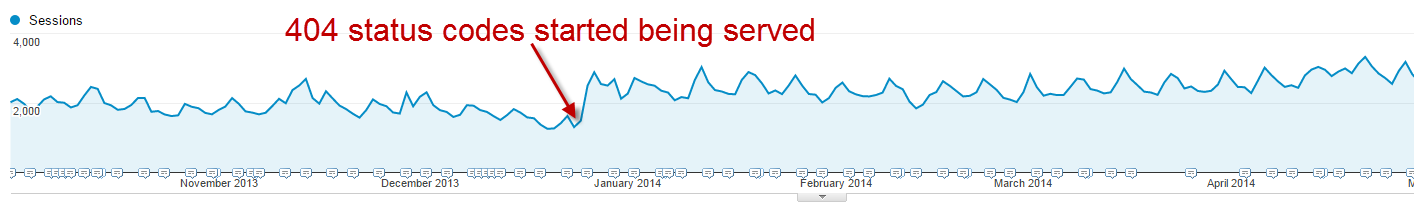
The story doesn’t end there folks. It turns out this client was using a custom website platform used by many other online retailers – meaning that other websites built by the developer were running on the same platform. So, when the developer started serving HTTP 404 status codes for any deleted pages on their platform, other businesses using that platform started reporting a sharp rise in their organic traffic. I can only assume that the web developers took all the credit for this, despite the month-long battle we had convincing them that soft 404s were worth resolving in the first place!
Soft 404s: The Importance of Technical SEO
Technical SEO is something many marketers are only vaguely familiar with. Indeed, even for SEO practitioners, it’s often an area that tends to fall into the hands of web developers. This can lead to huge missed opportunities in terms of improving organic search visibility. The technical functions of a website are what I’d consider the building blocks of SEO and as we’ve seen in the example above, they are especially important for enterprise-level e-commerce websites.
TL;DR – Too Long; Didn’t Read
- Whenever the 404 (not found) error message is displayed on a page, the server should return an HTTP 404 standard response code.
- The content of the page (the ‘page not found’ message) is entirely unrelated to the HTTP response returned by the server.
- A soft 404 error occurs when a non-existent page (a page that has been deleted/removed) displays a ‘page not found’ message to anyone trying to access it but doesn’t return an HTTP 404 status code. This can happen when the deleted page redirects users to an irrelevant page such as the website’s homepage.
- The number of soft 404s reported needs to be compared with the total number of indexable pages on a site – if this ratio of soft 404s/indexable pages is high, it can negatively impact a website’s performance in organic search by wasting valuable crawl budget.
- Resolving soft 404 issues can dramatically improve crawl efficiency and ensure search engines only spend time crawling the pages you want them to.
- Fixing your soft 404 errors can improve a website’s visibility in organic search.
Have you just learned something new?
Then join the 80,000 people who read our expert articles every month.








